OpenPMIx
Reference Implementation of the Process Management Interface Exascale (PMIx) standard
Downloads Privacy Policy Security Policy Publications Community ContributeRFC0002
Title
PMIx Event Notification
Abstract
The PMIx Event Notification system provides a mechanism by which the resource manager can communicate system events to applications, thus providing applications with an opportunity to generate an appropriate response. In addition, applications can use the system to request that the resource manager notify their peers of internal events (e.g., computational errors and aborted operations), and notify the resource manager of events detected by the application.
Labels
[MODIFICATION] [EXTENSION] [ORGANIZATION]
Action
[APPROVED]
Copyright Notice
Copyright (c) 2016 Intel, Inc. All rights reserved.
This document is subject to all provisions relating to code contributions to the PMIx community as defined in the community’s LICENSE file. Code Components extracted from this document must include the License text as described in that file.
Description
The resource manager will be aware of a wide range of events that occur across the system. For the purposes of this discussion, only events that impact the allocated session being served by the PMIx server are considered. These events can be divided into two distinct classes:
- Job-specific events that directly relate to a job executing within the session. This might include events such as debugger attachment or process failure within a related job. These events are characterized by directly targeting processes within session jobs – i.e., the “procs” parameter of the notification contain members of a job executing within the session. Events in this category are to be immediately delivered to the PMIx server library for delivery to the specified processes.
Clients can indicate a desire to register solely for job-specific events by including the PMIX_EVENT_JOB_LEVEL key in their call to PMIx_Register_event – i.e., providing this key will explicitly indicate that environment events are not to be reported to this callback function.
- Environment events that impact the session, but are not directly sent to executing jobs. This is a much broader category of events that includes ECC errors, temperature excursions, and other environmental events directly affecting the session’s resources. Note that although these do impact the session’s jobs, they are not directly referencing those jobs – i.e., the event is generated without specifying a particular target. Thus, events in this category are to be delivered to the PMIx server library only upon request – i.e., when the PMIx server has registered for those events.
Note that race conditions can cause the registration to come after events of possible interest (e.g., a memory ECC event that occurs after start of execution but prior to registration). RMs are free to cache events in this category for some time to mitigate this situation, but are not required to do so. Thus, applications must be aware that environment events prior to registration may not be included in notifications.
As above, clients can indicate a desire to register solely for environment events of a given type by include the PMIX_EVENT_ENVIRO_LEVEL key in their registration call.
The PMIx server will cache any environment and job-related events passed to it for a period of time to provide notification to clients that have not yet registered for them. Currently, the PMIx server uses a ring buffer to cache events. The size of the ring buffer defaults to 512 events (as of PMIx 2.0), but can be configured using the PMIx_server_cache_size info key during the call to the PMIx_Server_init API. Job-related events will be retained until all local clients have received them, regardless of the size or number of events being cached in the ring buffer. Of course, it is possible that enough job-related events could occur to “flood” the ring buffer, thereby causing events to be lost. A long-term solution to the “flood” problem remains as work-in-progress.
Client application processes can also use the PMIx Event Notification system to request that the resource manager notify its peers of internal events, and notify the resource manager of events detected by the application process. Examples of the latter include network communication errors that may not have been detected by the fabric manager itself (e.g., data corruption). The client must direct the notification to the appropriate target (RM or peers) using the corresponding range parameter.
Multiple event handlers registered against the same event are processed in a chain-like manner based on the order in which they were registered, as modified by directive. Registrations against specific event codes are processed first, followed by registrations against multiple event codes and then any default registrations. At each point in the chain, an event handler is called by the PMIx progress thread and given a function to call when that handler has completed its operation. The handler callback notifies PMIx that the handler is done, returning a status code to indicate the result of its work:
- PMIX_EVENT_NO_ACTION_TAKEN: indicates that the handler didn’t take any action on this event
- PMIX_EVENT_PARTIAL_ACTION_TAKEN: the handler took some action, but did not fully resolve the situation
- PMIX_EVENT_ACTION_DEFERRED: the handler has queued actions to be taken later
- PMIX_EVENT_ACTION_COMPLETE: the handler has completely resolved the event and no further handlers should be called
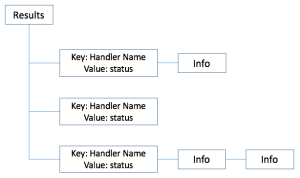
In addition to returning a status, each handler can return an array of pmix_info_t values that provide further information on the actions taken by that handler. The results are appended to the array of prior results, with the returned values combined into an array within a single pmix_info_t as follows:
- array[0]: the event handler name provided at registration (may be an empty field if a string name was not given) will be in the key, with the pmix_status_t value returned by the handler
- array[*]: the array of results returned by the handler, if any
There will always be a _pmix_info_t entry in the results array for each prior handler, and the array within that entry will always contain at least one element, as shown in the following diagram:
The following set of data is provided to each registered event handler:
- the event handler registration id returned when the handler was registered. This is provided in case the handler wishes to deregister itself upon invocation, and allows the handler to do so without having to lookup its id
- the status code for the event
- the pmix_proc_t identifying the source of the event. This will be the namespace/rank of the process that generated the event. The source will be NULL for events reported by the resource manager.
- an optional array of pmix_info_t containing any further info relating to the event
- an array of pmix_info_t containing the collected results from prior handlers in the chain, as shown above
- the callback function to be executed upon completing the handler’s actions
- a pointer to an object that is to be returned in the provided callback function
Note that the PMIx library itself does not register for event notifications. Internal events (e.g., unexpected client disconnect or message protocol failures) are resolved in code paths outside of the event notification system. However, such errors will generate events that can be received by the application and/or host resource manager if appropriate handlers have been registered.
Event Registration
Registration of event callbacks is accomplished via the PMIx_Register_event_handler API. The function takes the following set of parameters:
- An array of pmix_status_t error codes indicating which events should be passed to the specified handler. Multiple handlers can be registered against a given error code, and a given handler can be registered to receive notifications from any number of error codes. A NULL value for this parameter indicates registration of a default event handler for all error codes.
- An optional array of info keys providing directives regarding the
registration. These can include:
- PMIX_EVENT_HDLR_NAME: a string name identifying the registered handler. This value can be used for debugging purposes to record the status returned by the handler when called, and so that subsequent handlers (called during the precedence chain, as described below) can use the name and value when determining their response.
- PMIX_EVENT_JOB_LEVEL: a boolean indicating whether or not job-specific events are to be delivered to this handler. Job-specific events will be delivered to a registered handler by default.
- PMIX_EVENT_ENVIRO_LEVEL: a boolean indicating whether or not environmenal events are to be delivered to this handler. Default: false
- PMIX_EVENT_ORDER_PREPEND: a boolean flag directing that this callback be positioned first in precedence when considering events for the same error code. Default is to append the callback to the end of the current precedence list
- The event notification callback function to be called (i.e., the event handler)
- A callback function to be executed upon completion of the registration procedure
- A pointer to an object to be returned in the provided callback function
Registration of event callbacks that do not provide an array of info keys (beyond the optional PMIX_EVENT_HDLR_NAME) are considered default registrations for purposes of servicing order.
RM-Host Registrations
The RM host daemon is not required to register for any PMIx notifications. The daemon will automatically be notified (without registration) of client connection and finalize, plus any client service requests (including requests to distribute client-generated notifications), via the appropriate server callback functions, if provided. However, internal PMIx server errors (e.g., message protocol violations) will only be reported to the host RM if the RM daemon has registered for event notification, and will specify a NULL value for the target recipients.
Note that PMIx does request that the host RM daemon register for PMIx notifications so that any notifications targeted to the resource manager itself can be delivered.
Client Registrations
Application processes may request event notification via the PMIx_Register_event_handler API. Registrations are first recorded in the client’s notification callback stack based on the order in which calls to PMIx_Register_event_handler were issued, subject to adjustments per the provided info keys. This order will dictate the precedence given to event processing.
Once locally recorded, a registration request is sent to the local PMIx server for handling.
PMIx Server Registrations
The PMIx server acts as a proxy for client registrations. Once a registration request is received from a local client, the PMIx server records the registration and checks to see if the client is requesting notification of environmental events. If so, then the server checks to see if it is already registered with the host RM for matching events. If already registered, then no further action is required – otherwise, the PMIx server will register with the host RM for the specified events.
Once registration is complete, the server acks the request to the client, and then transmits any matching cached events to the client for local notification. Cached events are retained until the ring buffer becomes full, at which point the oldest events are ejected first.
Notifications
RM Notifications
PMIx expects that all RM notifications pertaining to an allocated session will be distributed to the RM daemons within that allocation. Job-specific events, and events for which the PMIx server has registered, are to be delivered upon receipt to the local PMIx server via the PMIx_Notify_event function. All environmental events are to be delivered to the PMIx server only if that server has previously registered for matching events.
Once the PMIx server has been notified of an event, it performs the following operations:
- for a job-specific event, the server immediately sends the event to its local clients from that job. If all local clients have been started, then the server can delete the event upon completion of notification. If any local clients for the job have not yet connected, then the server will cache the event for delivery upon connection, and delete it from the cache once all relevant processes have been notified.
- environment events are immediately sent to all clients who have registered for events that match the incoming event, and cached in the server’s ring buffer. If the ring buffer is full, then the oldest event will be ejected and released to make room. Upon receipt of a registration, the server will check that registration against all cached events, sending those that match back to the client.
Upon receipt of a notification message, the PMIx client will scan its list of registered callback functions to identify appropriate recipients according to the following precedence rules:
- registered callbacks for specific event codes that match the incoming one shall be serviced first. If multiple callbacks meet this criteria, then they will be processed according to their FIFO-based precedence when registered.
- registered callbacks for event groups that contain the incoming event are serviced next. Again, if multiple callbacks meet this criteria, then the same FIFO-based precendence rules are applied to them.
- default registered callbacks are serviced last.
The scan is continued until either a callback returns PMIX_EVENT_ACTION_COMPLETE, thereby indicating that the event has been handled and no further action is required, or all relevant callbacks have been executed. Return of any other status indicates that the procedure is to continue, with the returned status added to the results array passed along with the event. These updates are presented in a form where the key is the “name” given to the event callback (provided during registration), and the value is the returned status. Thus, subsequent event handlers can scan the incoming info key’s to see what prior event handlers reported.
Once the client has completed handling of an event, the received notification message is released. No return message is sent to the notifying server – it is assumed that any such action will be taken directly by an event handler if required.
Client-Based Notifications
The client may also choose to generate notifications, either by the application itself (e.g., informing its peers of some internal event) or by the PMIx client library for use by its host application. Examples of the latter include notification of loss of contact with the local PMIx server, which indicates that the process has become isolated and may be used to trigger a “suicide”.
Internal PMIx client library notifications are never transmitted to the local PMIx server. These notifications are only for use by the host application, and are provided based on registration by the application for events. Event registration by the client application does not differentiate between locally internal and external events. Thus, the user must differentiate by registering for specific internal error constants to separately respond to internal events. Currently supported internal events include:
- PMIX_ERR_LOST_SERVER_CONNECTION: Connection to the local PMIx server has been lost, usually indicating that the local server has failed
- PMIX_ERR_FAILED_COMM: Indicates either that a message from the local server could not be correctly unpacked, or that an outbound message could not be packed. In either case, the communication was unsuccessful.
Users are advised to check the release notes for their version for updates to this list.
Notifications generated by the application itself (via calls to PMIx_Notify_event) are transmitted to the local PMIx server for distribution. Since the PMIx server does not itself have the ability to communicate across nodes, it will pass the events on to the host RM daemon for distribution according to the provided _pmix_data_range_t parameter.
Protoype Implementation
The PMIx library implementation is covered in the PMIx Event Notification – Reimplementation pull request. The prototype has been tested against Open MPI as referenced in the Enable the PMIx event notification capability pull request.
Author(s)
Ralph H. Castain
Intel, Inc.
Github: rhc54